October 2025 Science Innovations: Nanotech, AI, Climate, and Space Breakthroughs
When you think about nanotechnology, the science of building and using materials at the atomic and molecular scale. Also known as nanotech, it's no longer just a lab curiosity—it's in your cancer drugs, your sunscreen, and the next generation of solar panels. In October 2025, Indian researchers made real progress in making nanomedicine more affordable and accessible, with new delivery systems for drugs like Doxil and Abraxane that target tumors without wrecking healthy tissue. This isn’t science fiction. It’s happening right now in labs across Bangalore, Pune, and Hyderabad.
Meanwhile, artificial intelligence, systems that mimic human reasoning to solve complex problems. Also known as AI, it's moving beyond chatbots and into real-world tools that help farmers, doctors, and engineers make better decisions. The big shift in 2025? Everyone’s asking not just what AI can do, but how much it actually costs. Hidden GPU bills, data labeling fees, and licensing traps are eating into budgets. That’s why posts this month broke down exactly what you pay for Gemini, foundation models, and edge AI—no fluff, just numbers. And if you’re wondering how AI ties into public health or agriculture, it’s simpler than you think: AI helps predict disease outbreaks, optimizes irrigation, and even spots crop pests from satellite images.
Then there’s climate change, the long-term shift in global temperatures and weather patterns caused by human activity. Also known as global warming, it’s not a future threat anymore—it’s here, and it’s changing how we live. October’s data showed CO₂ levels hitting new highs, wet-bulb temperatures creeping into dangerous zones, and sea level rise accelerating faster than models predicted. But it’s not all doom. Posts this month also highlighted practical fixes: hybrid solar systems that keep homes powered during blackouts, low-sugar diets that reduce heart disease risk, and how public health strategies are shifting from treatment to prevention. And yes, we looked at the most polluting renewable energy source too—turns out, biomass and big dams aren’t as clean as they seem.
And then there’s space. Not the stars. Not the rockets. The clothing. Female astronauts don’t wear bras in microgravity—they wear compression shirts designed for zero-G comfort. That’s the kind of detail you won’t find in Hollywood, but you’ll find it here. October’s posts dug into the real science behind everyday things: what jobs exist in agriculture beyond farming, how to become a medical scientist in 10 years, and why the 4 P’s of innovation—People, Process, Partnerships, Policy—are the real keys to lasting change, not just flashy gadgets.
This collection isn’t just a list of articles. It’s a snapshot of what’s working, what’s broken, and what’s next in Indian science. Whether you’re a student, a professional, or just curious, you’ll find something here that changes how you see the world around you. Below are the real stories behind the headlines—no hype, no filler, just facts.
Do Female Astronauts Wear Bras in Space? The Real Answer About Clothing in Microgravity
Oct, 30 2025
Female astronauts don't wear bras in space-instead, they use compression undershirts designed for comfort and function in microgravity. Here's how space clothing really works.
Read Article→What Are the 4 P's of Innovation? A Practical Guide to Policy and Practice
Oct, 30 2025
The 4 P's of innovation-People, Process, Partnerships, and Policy-are the real drivers of public innovation. Learn how they work together to create lasting change in communities, not just tech projects.
Read Article→What Drugs Use Nanoparticles? A Clear Guide to Nanomedicine Today
Oct, 28 2025
Nanoparticle drugs like Doxil, Abraxane, and Onivyde deliver chemotherapy more precisely, reduce side effects, and treat hard-to-reach cancers. Learn which medications use nanotechnology and how they're changing modern medicine.
Read Article→What Is the #1 Health Problem in the US?
Oct, 28 2025
Heart disease is the #1 health problem in the U.S., killing 702,000 people annually. It's preventable, but broken systems around food, stress, and inequality keep it thriving. Here’s what’s really behind the crisis-and what actually works.
Read Article→What Is an Agriculture Expert Called? Titles, Roles, and Career Paths
Oct, 26 2025
Learn the exact titles for agriculture experts-agronomist, agricultural scientist, farm manager, and more-plus duties, education, and career tips.
Read Article→Is Space Infinite? Exploring the Limits of the Cosmos
Oct, 25 2025
Explore whether space is truly endless, covering observable limits, curvature, dark energy, inflation, and future missions in an engaging, 1500‑word guide.
Read Article→Public Health Approach to Healthcare Explained
Oct, 24 2025
Discover how the public health approach shifts focus from treating illness to preventing disease, promoting equity, and improving community health outcomes.
Read Article→What jobs fall under agriculture? - Comprehensive guide to agricultural careers
Oct, 23 2025
Explore the full spectrum of agricultural jobs, from farm work to agri‑tech, with duties, education paths, salaries and growth outlook for each role.
Read Article→Home Solar Panels: Grid‑Tied, Off‑Grid & Hybrid Explained
Oct, 22 2025
Learn how home solar panels connect to the grid, batteries or both. We break down grid‑tied, off‑grid and hybrid systems, costs, regulations and best‑fit tips.
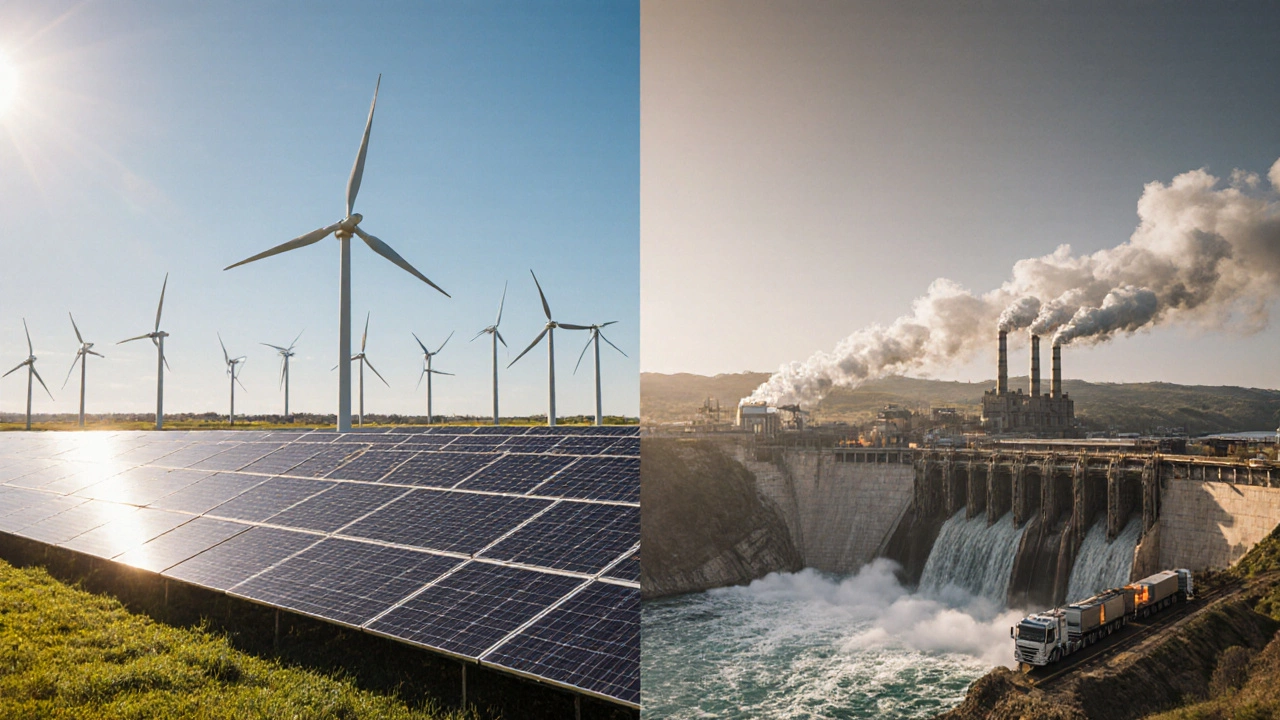
Read Article→Which Renewable Energy Source Has the Highest Pollution Impact?
Oct, 20 2025
Find out which renewable energy source has the highest lifecycle emissions and why biomass and large hydropower often top the pollution list.
Read Article→Is Earth Becoming Too Hot for Humans? Climate Change Facts & Risks
Oct, 19 2025
Explore how rising global temperatures threaten human habitability, the science behind wet‑bulb limits, and what actions can keep Earth safe for people.
Read Article→How Long Does It Take to Become a Medical Scientist? Timeline & Steps
Oct, 18 2025
Learn the typical timeline, education steps, and career paths to become a medical scientist, including degrees, funding, and alternative routes.
Read Article→